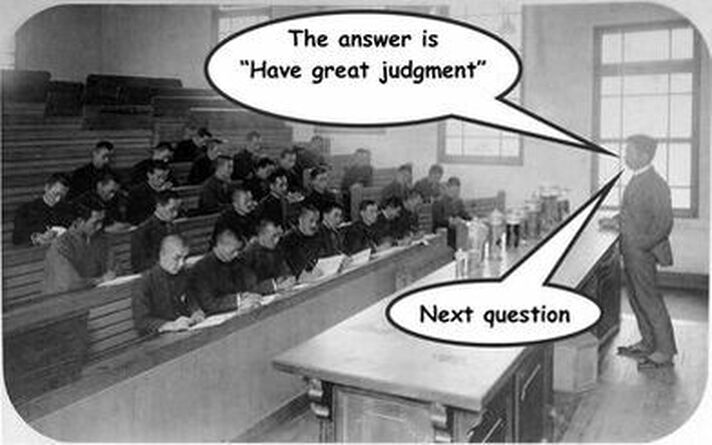
A close friend of mine believes successful PhD students have three things in common: They're smart, they work hard, and they have good judgment. The secret sauce here is "good judgment." Although smarts and hard work are important, most PhD students would have never been admitted if they weren't already smart, hard workers. But having good judgment is more elusive. It includes things like knowing what's "interesting" and what isn't, knowing what's worth worrying about (and what isn't), knowing what's important to prioritize, knowing how to solve a people problem, knowing whether to persist on a project or to move on, and so on. But advising a PhD student to "Have great judgment" is like advising a football team to "Score the most points." It doesn't tell them how. You can't say "Have great judgment" and then say "Next question," "QED," or drop the mic and walk out. Maybe there's two types of judgment -- technical judgments and nontechnical judgments. For graduate students, building technical judgment is about learning the whys of research. One way to build better technical judgment is to boldly ask lots of "Why?" questions of your mentor, advisor, or of an older student: "Why did you send it that journal? Why didn't you use a different method? Why did you ask the research question that way?" Most of us shied away from asking technical judgment questions because we didn't want to be irritating or look like we didn't belong. Most professors I know actually like to answer these questions, and they love to see an engaged student step out of a silent huddle. Developing good nontechnical judgment is trickier. Yet this is the critical judgment you need to troubleshoot how you can be a better teacher, or whether to choose the risky dissertation you want to do versus the safe dissertation your advisor wants. It involves figuring out how to deal with your off-the-chart stress level or whether you should take a job at a teaching college or go into industry. Our tendency as a graduate student is to get feedback from peers in our same year. A more effective one may be to get it from recent graduates or from professors who have seen cases like these and know how they worked out. You can even get nontechnical advice from professors you know in other departments. The best nontechnical dissertation advice I got was from a Medical School professor from my church. It was straightforward, unbiased, kind, and based on lots of students he had known. As professors, we can help to build better technical judgment by encouraging questions about our research judgment calls, or we can give it as color commentary or as context when we discuss a research project. But again, helping students with nontechnical judgments is trickier. One way to do this is in the third person. This can be by discussing a problem that "their friend" is having or by discussing a relatable case study. Here's one approach to building nontechnical judgment. I used to teach a PhD course where we'd meet in my home for a casual last class session. The first half of the session would be a discussion about graduate student success and the last half would be dinner. Each student had been asked to anonymously write down a dilemma that "one of their friends" was facing that was being a roadblock to their success. We'd mix these 9-10 dilemmas up, and we'd relax in the living room with a glass of wine and discuss them one at a time. For each one, we'd talk about similar experiences, options, solutions, and so forth. By dinner time, we had a more balanced perspective and some suggested next steps for many of the dilemmas. Over the years, it seemed that about 70% of these dilemmas were about the same 7-8 issues. These were like the issues mentioned above -- "risky vs. safe dissertation," "stress level," "leave academia," and so on.
Here's a second approach to building nontechnical judgment. Given how similar these dilemmas were from year to year, I wrote up 1-page PhD student case studies that involved slightly fictionalized people who were facing these common problems. These case studies were in the syllabus for the course, and we'd take the first or last part of each class to talk about that week's case study. The common dilemmas faced in your field may be different, but the enthusiasm your students would have in discussing them would probably be the same. Some people might be born with great judgment, but for the rest of us, it's a lot of trial and error and a lot of asking bold questions. If you're a graduate student, you've got a lot more license than you might think to learn from trial, error, and bold questions. If you're a professor, there's a lot we can do to help them. |
Welcome...Fun, useful, or wacky experiences about getting tenure, teaching better, publishing more, and having an incredibly rewarding career.
Categories
All
Some Blog ShortcutsArchives
September 2020
|


 RSS Feed
RSS Feed